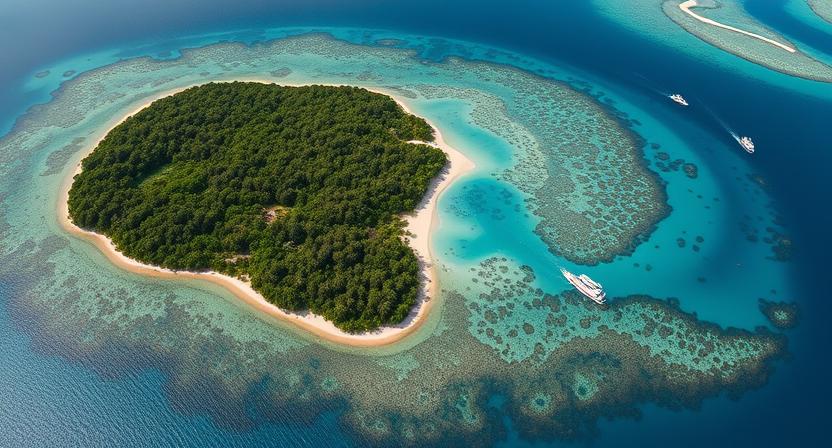
Yukevalo Island is an enigmatic and pristine destination that has slowly started gaining attention among eco-tourists and nature enthusiasts. Nestled in a secluded part of the ocean, Yukevalo Island remains largely untouched by commercial tourism, offering visitors a rare glimpse into an ecosystem that thrives in harmony with nature. This article delves into the geography, ecology, history, cultural significance, and potential for sustainable tourism of Yukevalo Island.
Table of Contents
Geography and Location
Yukevalo Island is located in a remote part of the [specific ocean or sea—user can insert accurate location if known]. The island spans approximately 15 square kilometers, making it small enough to explore on foot yet large enough to host a variety of unique habitats. The island’s topography is characterized by gentle rolling hills, dense tropical forests, sandy beaches, and hidden coves. Small freshwater streams flow from the island’s central hills to the surrounding ocean, creating ideal habitats for freshwater species and supporting the island’s biodiversity.
The climate of Yukevalo Island is tropical, with warm temperatures year-round. Rainfall is seasonal, typically peaking during the monsoon months. This combination of sun and rain allows the island to sustain lush vegetation and a vibrant ecosystem.
Flora and Fauna
One of the most fascinating aspects of Yukevalo Island is its biodiversity. The island is home to numerous endemic plant and animal species that cannot be found anywhere else in the world. Dense mangroves along the coast provide shelter for a variety of bird species, while the interior forests are home to rare orchids, towering trees, and medicinal plants used by local communities.
The fauna on Yukevalo Island is equally impressive. Birdwatchers can spot colorful species such as kingfishers, parrots, and the elusive Yukevalo finch. Mammals, including small primates, wild boars, and fruit bats, roam the forests freely. The surrounding coral reefs host a diverse range of marine life, from clownfish and sea turtles to larger predators like reef sharks. This unique biodiversity makes Yukevalo Island a hotspot for ecological studies and conservation efforts.
History and Cultural Significance
Although largely uninhabited today, Yukevalo Island has a rich historical and cultural background. Archaeological evidence suggests that indigenous peoples once settled on the island, leaving behind artifacts, cave paintings, and ceremonial sites. These findings indicate that the island played a role in regional trade and cultural exchanges, with early inhabitants relying on fishing, foraging, and small-scale agriculture.
Local folklore tells stories of the island as a mystical place where nature spirits reside. These legends have contributed to the island’s reputation as a sacred site, and some traditional practices still honor the spiritual significance of the island. Preservation of this cultural heritage is essential not only for historians but also for visitors who wish to understand the deep connections between humans and nature on Yukevalo Island.
Tourism Potential and Eco-Friendly Activities
Yukevalo Island has significant potential for eco-tourism. Its natural beauty, combined with its relatively untouched ecosystems, makes it an ideal destination for responsible travelers. Visitors can enjoy activities such as guided hikes, birdwatching tours, snorkeling, and kayaking in the calm coastal waters.
Conservation efforts are critical to maintaining the island’s ecological balance. Local authorities and environmental organizations have implemented guidelines for sustainable tourism, such as limiting the number of visitors at any given time, establishing eco-lodges instead of large hotels, and promoting awareness about the importance of preserving the island’s biodiversity.
In addition to eco-tourism, Yukevalo Island offers opportunities for scientific research. Biologists, marine ecologists, and conservationists can study the island’s unique flora and fauna, helping to protect endangered species and restore natural habitats. This dual focus on tourism and research ensures that Yukevalo Island remains both an accessible destination and a sanctuary for wildlife.
Accessibility
Access to Yukevalo Island is intentionally limited to preserve its natural environment. Visitors usually reach the island by small boats or ferries from nearby coastal towns. The journey itself is scenic, offering views of the open ocean, passing dolphins, and occasional seabird flocks. Once on the island, walking trails and guided tours allow exploration without disturbing sensitive areas.
For those interested in extended stays, eco-lodges provide basic yet comfortable accommodations with minimal environmental impact. Solar panels, rainwater collection systems, and composting facilities are commonly used to reduce the ecological footprint of tourism.
Conservation Challenges
Despite its isolation, Yukevalo Island faces several conservation challenges. Climate change and rising sea levels threaten the island’s coastal habitats, while illegal fishing and poaching could disrupt the delicate ecosystem. Human activities, if not carefully managed, have the potential to degrade the island’s natural beauty and biodiversity.
Conservationists emphasize the importance of community involvement in protecting Yukevalo Island. Local populations can benefit from sustainable tourism initiatives while also acting as stewards of the environment. Educational programs for both locals and visitors help raise awareness about the importance of preserving the island’s unique ecosystems.
Future Prospects
The future of Yukevalo Island depends on balancing environmental protection with responsible tourism. With proper planning, the island can serve as a model for sustainable travel and conservation. By fostering eco-friendly tourism, supporting research initiatives, and honoring cultural heritage, Yukevalo Island has the potential to remain a hidden gem for generations to come.
The growing interest in sustainable travel presents an opportunity to showcase Yukevalo Island as a destination where nature and humans coexist harmoniously. By maintaining strict conservation standards, encouraging educational tourism, and promoting cultural awareness, the island can continue to enchant visitors while safeguarding its rich biodiversity.
FAQs About Yukevalo Island
1. Where is Yukevalo Island located?
Yukevalo Island is situated in a remote part of the [insert ocean/sea], known for its pristine natural environment and biodiversity.
2. What makes Yukevalo Island special?
The island is notable for its endemic species, untouched ecosystems, and cultural heritage sites that reflect the history of early inhabitants.
3. Can tourists visit Yukevalo Island?
Yes, tourism is allowed but strictly regulated. Visitors can enjoy eco-friendly activities such as hiking, birdwatching, and snorkeling.
4. What kind of wildlife can be found on Yukevalo Island?
The island hosts a wide range of species including colorful birds, small primates, wild boars, fruit bats, and marine life in the surrounding coral reefs.
5. How is the island protected?
Conservation measures include limiting visitors, promoting eco-lodges, and involving local communities in environmental stewardship.
6. What are the accommodation options on Yukevalo Island?
Eco-lodges are the primary accommodation, featuring sustainable infrastructure such as solar panels and rainwater harvesting systems.
7. Why is Yukevalo Island important for research?
Its unique ecosystems make it an ideal site for studying biodiversity, conservation strategies, and climate change impacts on isolated habitats.