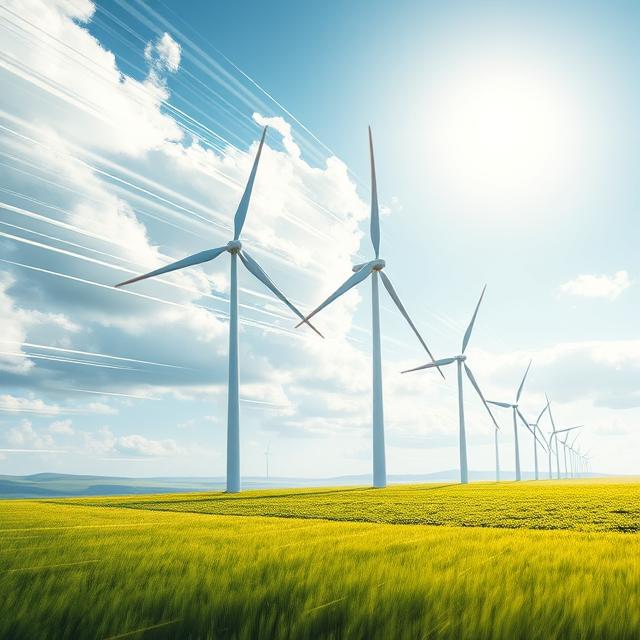
The term “speedwind” is not one that most people encounter in their everyday vocabulary, yet it carries an intriguing meaning depending on its context. While it may sound like a reference to natural wind patterns, in reality, speedwind is often used in discussions involving technology, performance, and even environmental sciences. The concept brings together ideas of motion, velocity, and energy transfer, making it valuable in multiple domains such as renewable energy, mechanical engineering, sports dynamics, and modern design thinking.
This article explores the origins, implications, and applications of speedwind, breaking down how it affects human life, industry, and innovation.
Table of Contents
What Does Speedwind Mean?
At its core, the word speedwind refers to a rapid flow of air or movement of force that carries both speed and direction. Depending on the context, it can be described in different ways:
- Natural Context – Wind traveling at high speed due to atmospheric pressure differences.
- Engineering Context – Mechanical systems that generate or harness rapid airflow, such as turbines or high-speed fans.
- Metaphorical Context – A figurative expression used to describe progress, acceleration, or momentum.
Thus, speedwind is both a literal and symbolic term, bridging the natural and technological worlds.
The Science Behind Speedwind
Atmospheric Speedwind
In meteorology, speedwind can be explained as the movement of air masses at high velocities. Jet streams in the upper atmosphere are a perfect example. These narrow bands of strong winds move at speeds exceeding 100 miles per hour, influencing weather systems across the globe. Speedwind in this sense plays a role in aviation, climate regulation, and storm formation.
Mechanical Speedwind
In engineering, speedwind describes the rapid circulation of air created by machines. For instance:
- Wind turbines rely on natural wind speed, but efficiency often depends on how well they capture speedwind.
- Automotive designs test vehicles in wind tunnels, where speedwind simulations reveal aerodynamic strengths and weaknesses.
- Industrial cooling systems use speedwind principles to manage heat dissipation in machines.
Energy and Speedwind
One of the most promising applications of speedwind is in the renewable energy sector. High-speed winds are harnessed by turbines to generate electricity. The faster the wind speed, the more kinetic energy can be converted into usable power. This makes speedwind a valuable resource in the global shift toward sustainable energy.
Speedwind in Human Innovation
Transportation and Aerodynamics
The speedwind principle shapes transportation technologies, especially in aviation and automotive industries. Aircraft rely on the balance between airspeed and lift, while modern car designs minimize drag to maximize fuel efficiency. Speedwind analysis ensures safer, faster, and more sustainable travel.
Sports and Performance
Athletes also experience the effects of speedwind. Cyclists and runners train with wind resistance in mind, as headwinds can slow performance while tailwinds provide a natural boost. Even sailing competitions revolve around mastering the force of speedwind to achieve optimal movement.
Architecture and Urban Planning
Modern architects design skyscrapers, bridges, and urban structures with speedwind considerations. Strong wind currents can destabilize tall structures if not accounted for. Engineers use simulations to test how speedwind affects stability, safety, and long-term durability.
Symbolic and Cultural Dimensions of Speedwind
Beyond science and engineering, speedwind is a metaphor that captures the essence of progress and acceleration. Writers, poets, and motivational speakers often use it as a symbol of momentum, freedom, and unstoppable energy.
- In literature, speedwind may represent unstoppable change or a journey of transformation.
- In philosophy, it can be linked with the flow of life, pushing individuals toward growth and new horizons.
- In modern culture, speedwind resonates with themes of innovation, futuristic progress, and limitless possibilities.
Challenges Related to Speedwind
Environmental Concerns
Harnessing speedwind energy is sustainable, but large-scale wind farms can create ecological disruptions. Birds and bats are often affected by turbine blades, and the noise generated can disturb local communities.
Structural Risks
Excessive speedwind in urban environments can be dangerous. Strong gusts can damage buildings, uproot trees, and disrupt daily life. Engineers and city planners must account for these risks in design.
Economic Considerations
Although speedwind is free in nature, capturing and converting it into usable forms requires costly infrastructure. Wind farms, aerodynamic testing facilities, and specialized machinery demand significant investment.
The Future of Speedwind Technology
- Next-Generation Wind Energy – With advances in turbine design, speedwind energy can become even more efficient and widely accessible.
- Aerospace Applications – Hypersonic aircraft research depends heavily on understanding speedwind at extreme velocities.
- Smart Cities – Urban planning of the future will use speedwind data to design safer, greener, and more energy-efficient spaces.
- Sports Science – Wearable technologies may soon allow athletes to measure speedwind resistance in real time, improving performance.
Conclusion
The concept of speedwind combines the forces of nature with human innovation. Whether in the form of jet streams guiding global weather, turbines generating renewable energy, or aerodynamic designs shaping future technologies, speedwind influences countless aspects of life.
As science and society move forward, speedwind will remain a key factor in energy, transportation, performance, and culture. Understanding and harnessing it effectively ensures not only technological progress but also a sustainable future.
FAQs About Speedwind
Q1: Is speedwind a scientific term or just a metaphor?
Speedwind can be both. In science, it often refers to high-speed winds in nature or airflow in mechanical systems. Metaphorically, it represents progress, acceleration, and unstoppable energy.
Q2: How is speedwind related to renewable energy?
Wind turbines depend on strong, consistent wind speeds—known as speedwind—to generate electricity efficiently.
Q3: Can speedwind affect human health?
Not directly, but excessive wind speeds can contribute to discomfort, allergies (through airborne particles), and in extreme cases, accidents.
Q4: What role does speedwind play in sports?
In athletics, speedwind resistance influences performance. Runners, cyclists, and sailors adjust their strategies depending on wind speed and direction.
Q5: How is speedwind managed in cities?
Urban planners use simulations to understand airflow around buildings. This helps prevent dangerous wind tunnels and improves safety in high-rise areas.