Different sweeteners are digested by the human body in various ways. The distinction between stevia and artificial and other sweeteners is frequently not made explicit, making comparisons between them confusing.
Let’s first examine how the body breaks down sugar. The pancreas generates insulin to break down sugar after digestion, which regulates blood sugar levels. This is particularly problematic for diabetics since low insulin production results in inadequate sugar breakdown, which raises blood sugar levels.
Stevia Rebaudiana Bertoni is a plant native to Paraguay and Brazil that produces a number of sweet chemicals, including stevioside and rebaudioside A (often known as Reb-A), two glycosides. Stevia Sweeteners are a non-calorie substance with a high solubility and a good flavour profile that have been used in Japan for more than 40 years. We’re going to discuss stevia powder Eartho maya and digestion in this article.
Stevia’s metabolism and excretion have been investigated in both humans and animals. According to these studies, stevia can be used as a common sweetener in food without any risks. Here is a succinct explanation of how stevia works.
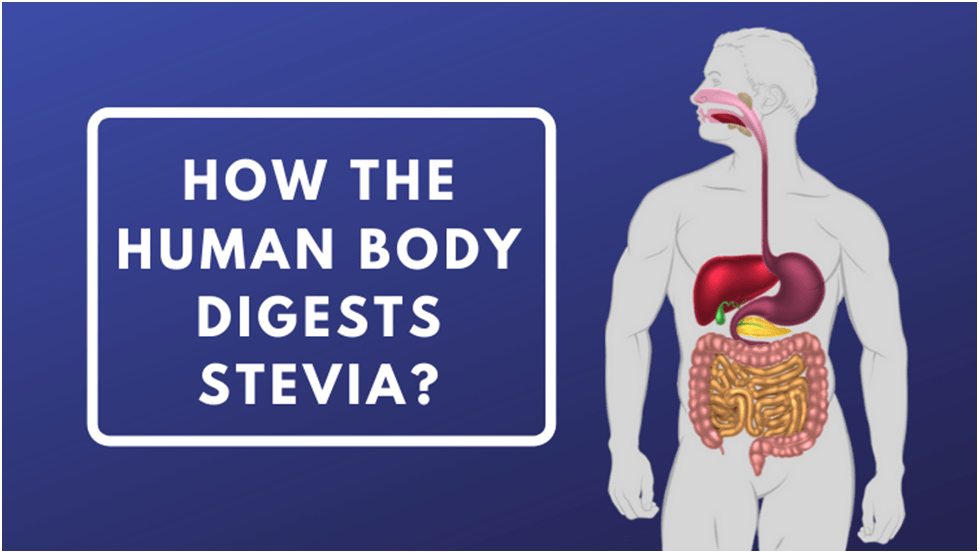
Reb-A is first broken down by the bacteria in the colon to the luminal side, where it is subsequently transformed to steviol, which releases a glucose molecule. The exposed glucose molecule is not absorbed; instead, it is used by colonic bacteria. Since steviol glycosides are metabolised in steviol, the metabolic equivalents of various steviol glycosides enable the application of findings from stevioside studies to the evaluation of Reb-safety. A’s
Different metabolites of stevia exist. The steviol glycosides pass through the body untouched (as opposed to sugar) down to the colon where the glycoside is gradually eliminated by hydrolysis to produce steviol. Since the body does not react to stevia as it does with sucrose from sugar, there is no insulin production.

The liver receives the steviol through the blood, where it is transported and combined with glucuronic acid to create steviol glucuronide. The steviol glucuronide is eliminated in the urine after passing through the kidneys. The body does not accumulate steviol glycosides. Urine and faeces are the means by which the body expels everything that is taken in.
buy finasteride online https://idhfa.org/pdfs/new/finasteride.html no prescription
Although there are some differences between the species, it has been demonstrated that the conversion rate of Reb-A and stevioside from stevioside to that of Reb-A is comparable in rats and humans. Additionally, both quantitative and qualitative parallels between the microbiota of rats’ intestines and that of humans are discovered. Additionally, both short- and long-term studies have been done in-depth research on the toxicity of stevia.
Importantly, no significant carcinogenic, genotoxic, or toxic consequences have been found in mammals. Human faeces demonstrate that steviol, the end product of stevia metabolism, does not alter or change. According to studies, the liver metabolises the majority of these compound glycosides into glucuronidation (a bond created to help cleanse them from the blood). The molecular component helps the colon eliminate a modest amount of glucuronides

Blood sugar levels rise as a result of sugar, and insulin is produced by the pancreas to help break down the sugar. Obesity, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, and diabetic issues can all result from excessive consumption.
Serotonin levels are impacted by aspartame, which impacts how hungry you feel. So, if being calorie-free can result in an increase in calories from other sources, what function does being calorie-free serve? Research reveals a wide range of other negative consequences, including carcinogenic and neurotoxic ones.
Stevia does not build up in the body, and studies show that it stimulates the synthesis of insulin.
Stevia has very little impact on metabolism and little negative side effects. Reb-made stevia products are also deemed safe for diabetics and expectant mothers. You don’t have to put it in everything because it is sweeter than sugar, so keep that in mind as well. It has been thoroughly investigated in a number of sectors and has been demonstrated to be safe for stevia digestion in people.
You can use one pinch of stevia powder for one teaspoon of sugar in your everyday cup of tea or coffee. Your favourite foods and drinks, such as coffee, tea, homemade lemonade, hot or cold cereal, even clean yoghurt, can all benefit from its inclusion. Stevia can also be used in baking. However, not all stevia brands are designed for baking, and some kinds can have a licorice-like aftertaste.
Sugar leaf or candy leaf plants contain stevia, a common sugar substitute. These plants’ leaves contain steviol glycosides, which are believed to be between 30 and 150 times sweeter than sugar. As a natural alternative to sugar, stevia is very well-liked all around the world, and many people substitute artificial sweeteners for it. As it has nearly no calories, it is frequently referred to as a healthy dessert.

