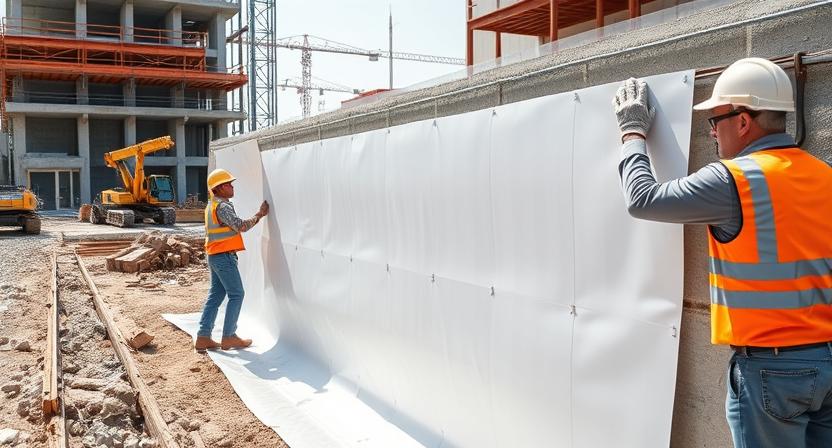
Polypropylene (PP) foundation systems represent a revolutionary approach to modern construction, offering unique advantages over traditional foundation materials. PP foundation refers to the use of polypropylene materials in various foundation applications, from waterproofing membranes to structural components that provide enhanced durability and performance in building foundations.
The construction industry has increasingly recognized the value of polypropylene-based foundation solutions due to their exceptional chemical resistance, flexibility, and longevity. These systems have transformed how engineers and architects approach foundation design, particularly in challenging environmental conditions where traditional materials might fail.
Table of Contents
What is Polypropylene in Construction Context?
Material Properties and Characteristics
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer that exhibits remarkable properties making it ideal for foundation applications. This synthetic material offers excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and environmental stressors that commonly affect building foundations. The molecular structure of polypropylene provides inherent flexibility while maintaining structural integrity under various load conditions.
The material’s low permeability to water vapor and liquids makes it particularly valuable in foundation waterproofing applications. Unlike traditional materials that may degrade over time when exposed to soil chemicals or groundwater, polypropylene maintains its protective properties for decades without significant deterioration.
Manufacturing Process and Quality Standards
PP foundation materials undergo rigorous manufacturing processes that ensure consistent quality and performance. The production involves precise temperature control and polymer chain alignment to achieve optimal mechanical properties. Quality standards for PP foundation materials typically include specifications for tensile strength, elongation capacity, and chemical resistance.
Modern manufacturing techniques allow for the production of PP foundation materials in various forms, including sheets, membranes, and molded components. Each form is engineered to meet specific foundation requirements while maintaining the core benefits of polypropylene technology.
Types of PP Foundation Applications
Waterproofing Membranes
PP waterproofing membranes represent one of the most common applications in foundation systems. These membranes create an impermeable barrier between the foundation structure and surrounding soil, preventing water infiltration that could compromise structural integrity. The flexibility of polypropylene allows these membranes to accommodate minor structural movements without tearing or losing their protective properties.
The installation of PP waterproofing membranes requires careful attention to seaming and attachment methods. Proper installation techniques ensure continuous protection and maximize the membrane’s lifespan. These systems often incorporate specialized adhesives and mechanical fasteners designed specifically for polypropylene materials.
Drainage Systems and Components
PP foundation systems frequently incorporate drainage components that manage groundwater and surface water around building foundations. These components include drainage boards, collection systems, and protective layers that work together to direct water away from foundation walls and footings.
The chemical inertness of polypropylene makes it ideal for drainage applications where the material may contact various soil chemicals or treated water. Unlike metal drainage components that may corrode over time, PP drainage systems maintain their functionality throughout the building’s lifespan.
Protective Barriers and Shields
Polypropylene protective barriers serve as shields against various environmental threats to foundation systems. These barriers protect against root intrusion, chemical attack from soil contaminants, and mechanical damage during backfilling operations. The tough, puncture-resistant nature of PP materials provides reliable long-term protection for sensitive foundation components.
Advantages of PP Foundation Systems
Superior Chemical Resistance
One of the most significant advantages of PP foundation systems is their exceptional resistance to chemical attack. Polypropylene remains stable when exposed to acids, bases, salts, and organic solvents commonly found in soil environments. This chemical stability ensures that the foundation protection system maintains its integrity regardless of soil chemistry variations.
Traditional foundation materials like rubber or modified bitumen may degrade when exposed to certain soil chemicals, leading to premature failure and costly repairs. PP foundation systems eliminate this concern by providing consistent performance across a wide range of chemical environments.
Exceptional Durability and Longevity
PP foundation materials offer remarkable durability, often outlasting the buildings they protect. Laboratory testing and field experience demonstrate that properly installed polypropylene foundation systems can provide effective protection for 50 years or more without significant degradation.
The material’s resistance to UV radiation, when properly formulated, ensures that exposed portions of the foundation system remain stable during construction and throughout the building’s life. This durability translates to reduced maintenance costs and improved building performance over time.
Flexibility and Thermal Stability
Polypropylene’s inherent flexibility allows foundation systems to accommodate structural movements caused by thermal expansion, settling, or seismic activity. This flexibility prevents cracking and failure that might occur with more rigid foundation materials.
The thermal stability of PP materials ensures consistent performance across a wide temperature range. From freeze-thaw cycles to high-temperature conditions, polypropylene foundation systems maintain their protective properties without becoming brittle or losing adhesion.
Installation Methods and Best Practices
Site Preparation and Planning
Successful PP foundation installation begins with thorough site preparation and careful planning. The foundation substrate must be properly prepared to ensure optimal adhesion and performance of the polypropylene system. This preparation includes surface cleaning, moisture control, and verification of substrate integrity.
Installation planning should consider environmental conditions, material handling requirements, and sequencing of construction activities. Proper planning minimizes installation delays and ensures that the PP foundation system achieves its designed performance characteristics.
Installation Techniques and Quality Control
Professional installation of PP foundation systems requires specialized techniques and equipment. Seaming methods, adhesive application, and mechanical attachment procedures must follow manufacturer specifications to ensure system integrity. Quality control measures during installation include seam testing, adhesion verification, and visual inspection protocols.
Temperature and humidity conditions during installation can significantly affect the performance of adhesives and sealants used with PP foundation systems. Installation procedures should account for these environmental factors to achieve optimal results.
Maintenance and Long-term Performance
Inspection and Monitoring Protocols
While PP foundation systems require minimal maintenance, periodic inspection helps ensure continued performance and identifies any issues before they become serious problems. Inspection protocols should focus on seam integrity, drainage system functionality, and overall system condition.
Modern monitoring technologies can be integrated with PP foundation systems to provide continuous feedback on system performance. These technologies help building owners understand foundation conditions and make informed maintenance decisions.
Repair and Rehabilitation Procedures
When repairs are necessary, PP foundation systems offer advantages in terms of repairability and compatibility with existing materials. Repair procedures typically involve cleaning, surface preparation, and application of compatible patching materials or replacement sections.
The chemical compatibility of polypropylene repair materials with existing PP foundation components ensures long-lasting repairs that maintain system integrity. Proper repair techniques can restore full system performance and extend the foundation system’s service life.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Recyclability and Environmental Impact
Polypropylene materials used in foundation systems are fully recyclable, contributing to sustainable construction practices. At the end of a building’s life cycle, PP foundation materials can be recovered and processed into new products, reducing waste and environmental impact.
The production of polypropylene requires less energy compared to many alternative materials, further enhancing its environmental credentials. Life cycle assessments consistently show favorable environmental profiles for PP foundation systems compared to traditional alternatives.
Green Building Integration
PP foundation systems contribute to green building certifications through their durability, energy efficiency benefits, and sustainable material characteristics. These systems help buildings achieve higher performance ratings while reducing long-term environmental impact.
The moisture control provided by PP foundation systems can improve building energy efficiency by preventing unwanted moisture infiltration that could compromise insulation performance or lead to mold growth.
Cost Analysis and Economic Benefits
Initial Investment Considerations
While PP foundation systems may have higher initial costs compared to some traditional alternatives, the long-term economic benefits often justify the investment. The durability and low maintenance requirements of polypropylene systems result in lower life cycle costs and improved return on investment.
Cost analysis should consider not only material and installation costs but also long-term maintenance expenses, potential repair costs, and the value of improved building performance. When evaluated on a life cycle basis, PP foundation systems frequently provide superior economic value.
Long-term Economic Value
The extended service life of PP foundation systems translates to significant economic benefits over time. Reduced maintenance requirements, fewer repairs, and consistent performance contribute to lower total cost of ownership for building foundations.
Insurance considerations may also favor buildings with high-performance foundation systems, as these systems reduce the risk of water damage and related claims. Some insurers offer premium reductions for buildings with proven foundation protection systems.
Future Developments and Innovations
Advanced Material Technologies
Ongoing research and development in polypropylene chemistry continue to improve the performance characteristics of PP foundation materials. Advanced formulations offer enhanced UV resistance, improved flexibility at low temperatures, and increased puncture resistance.
Nanotechnology applications are being explored to further enhance the barrier properties and durability of PP foundation systems. These innovations promise even better performance and longer service lives for future applications.
Smart Foundation Systems
Integration of sensors and monitoring technologies with PP foundation systems represents an emerging trend in smart building design. These systems can provide real-time data on foundation conditions, moisture levels, and system performance.
Smart PP foundation systems enable predictive maintenance strategies that optimize building performance while minimizing maintenance costs. This technology integration represents the future of high-performance building foundations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the expected lifespan of a PP foundation system?
PP foundation systems are designed to provide effective protection for 50+ years under normal conditions. The actual lifespan depends on installation quality, environmental conditions, and maintenance practices. Properly installed systems often outlast the buildings they protect.
Can PP foundation systems be installed in all climates?
Yes, polypropylene foundation systems are suitable for all climate conditions. The material’s thermal stability and flexibility allow it to perform effectively in extreme cold and hot climates. Specific product formulations may be recommended for particular environmental conditions.
How does PP foundation compare to traditional waterproofing methods?
PP foundation systems offer superior chemical resistance, flexibility, and longevity compared to traditional methods like modified bitumen or rubber membranes. While initial costs may be higher, the long-term performance and reduced maintenance make PP systems more economical over time.
Are PP foundation systems environmentally friendly?
Yes, polypropylene is fully recyclable and has a relatively low environmental impact during production. PP foundation systems contribute to sustainable construction practices and can help buildings achieve green certification credits.
What maintenance is required for PP foundation systems?
PP foundation systems require minimal maintenance. Periodic inspections to check seam integrity and drainage system functionality are recommended. The chemical inertness of polypropylene means the material doesn’t degrade under normal soil conditions.
Can PP foundation systems be repaired if damaged?
Yes, PP foundation systems can be effectively repaired using compatible materials and proper techniques. The thermoplastic nature of polypropylene allows for heat welding repairs that restore full system integrity.
How are PP foundation systems installed?
Installation requires specialized techniques including proper surface preparation, seaming methods, and quality control procedures. Professional installation by trained contractors is essential to achieve optimal system performance.
What building types benefit most from PP foundation systems?
PP foundation systems are beneficial for all building types but are particularly valuable for structures exposed to harsh soil conditions, chemical environments, or where long-term durability is critical. Commercial, industrial, and high-performance residential buildings commonly use these systems.